Though our body gets cool itself through sweating in a natural way. During hot weather particularly in high humidity, sweating just isn’t enough. Body temperature can rise to dangerous levels and develop heat illness. Most heat illnesses occur from staying out in heat too long, exercising much per your age and physical condition too matter.
Heat-related illnesses include.
• Heat stroke ~ a life-threatening illness in which body temperature rises with symptoms include dry skin, rapid, strong pulse, and dizziness
• Heat exhaustion ~ an illness that can precede heat stroke; symptoms include heavy sweating, rapid breathing, and a fast, weak pulse
• Heat cramps ~ muscle pains, spasms that happen during heavy exercise
• Heat rash ~ skin irritation from excessive sweating
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention previews: Heat intolerance is the inability to be comfortable when external temperatures rise.
Considerations: Heat intolerance often produces a feeling of being overheated and can cause heavy sweating, which usually comes on slowly and lasts over the long-term.
Symptoms:
• Behavioral changes as confusion, disorientation, or staggering
• Breathing shallow
• Dizziness and light-headedness
• Fainting
• Lack of sweating despite the heat
• Muscles weakness or cramps
• Nausea and vomiting
• Rapid heartbeat
• Red, hot, and dry skin
• Seizures
• Throbbing headache
• Unconsciousness
Causes:
• Age related physiological changes
• Alcohol or heavy meals
• Amphetamines such as appetite suppressant
• Caffeine
• Dehydration
• Excess thyroid hormone [thyrotoxicosis]
• Menopause
Home Care:
Preventive measures include drinking plenty of cool liquids and avoiding excessive heat and humidity, especially in unventilated spaces such as parked cars that can overheat quickly. Treatment requires rapid physical cooling of the body. The risk of heat stroke can be reduced by observing precautions to avoid overheating and dehydration.
• Avoid dehydration
• Clothing such as plastic fabrics that are impermeable to sweat and thus do not help heat loss through evaporation can give to heat stress
• Drink more fluids, replenishing salt, minerals and limiting time in the heat can help. Better to drink fluids often, and before you are thirsty
• In environments that are not only hot but also humid, it is important to recognize that humidity reduces the degree to which body can lose heat by evaporation. In such environments, it helps to wear light clothing such as cotton in light colors that is pervious to sweat but impervious to radiant heat from sun. This minimizes the gaining of radiant heat, while allowing as much evaporation to occur, as the environment will allow.
• In hot weather, people need to drink plenty of cool liquids to replace fluids lost from sweating. Thirst is not a reliable sign that a person needs fluids. A better indicator is the color of urine. A dark yellow color may indicate dehydration. Associated complaints as dizziness, fainting, palpitations, rapid pulse (heart rate), vomiting.
• Keep room temperature at a comfortable level
• Light, loose-fitting clothing enhance perspiration to evaporate and cool the body
• Strenuous exercise should be avoided during daylight hours in hot weather
Tests that may be performed include: Blood studies. Thyroid studies [TSH, T3, free T4]
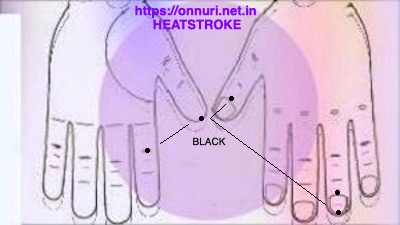
A powerful tool, colors ‘seed’ ONNURI that aide in controlling syndromes relates to HEAT stroke, or sensitivity to heat, by putting color with marker pen twice a day! Besides this may keep all toes nail with black color marker only. Try, and believe! Be of the opinion, and submit your episode, to make research more authenticated!
https://onnuri.net.in ‘Dr Dinesh kapur’
Believe in Cure!